- April 28, 2025
- 1:40 pm
- 0 comments
Table of Contents
A Guide to Parts of Speech and Their Role in English Grammar
Knowing English grammar is not just about knowing what tenses to use, it is also about developing communication skills. Whether it is written or spoken, to be coherent and make sense, you need to know English grammar and parts of speech are the cornerstone of it.
Parts of speech in English are the foundation on which effective communication is built. Parts of speech categorise words based on their function in a sentence and are a key part of the IB curriculum. They inform children about the grammatical framework and help them develop proficiency in English, the language with a global prevalence. In this guide, we will be diving deep to understand all parts of speech and how they are used. So, scroll down to learn how parts of speech work and their role in English grammar!
Why Are Parts of Speech Important in English?
International Baccalaureate schools in Bangalore focus on teaching all parts of speech, as without them, it is impossible to master the English language. Here is why they are absolutely important to developing crucial language skills that will benefit in the long term.
- Knowing all parts of speech helps improve writing. It facilitates the creation of well-structured and grammatically correct sentences.
- Parts of speech also help make sense of different sentences. It can improve the meaning a child derives from reading.
- Using proper grammar also helps in constructing sentences when speaking.
- Parts of speech in English also play a crucial role in reducing miscommunication and misunderstanding of texts.
Knowing parts of speech is certainly a crucial part of developing language and communication skills in a child. It helps children understand how to put their thoughts on paper in the proper way. Each part of speech in English has its own role, which we will be exploring further below.
What Are the Different Types of Parts of Speech?

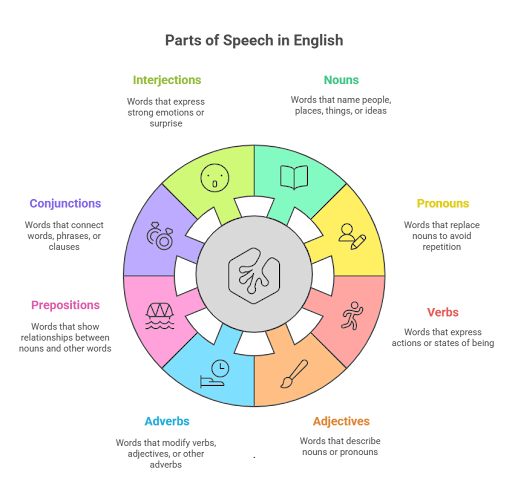
There are eight parts of speech in the English language. They help make a coherent sentence and are crucial in conveying meaning and adding more nuance to written or spoken words. Let’s take a look at the different types of parts of speech in English below,
Nouns – The Naming Words
Nouns are words that represent a person, place, thing, or idea. They are generally the subject of a sentence around which something is happening. It includes everything or everyone which have a name and can be seen, tasted, heard, touched, or smelled.
Types of Nouns
There are six major types of nouns in the English language –
- Proper Nouns: Specific names of people, places, or organisations and these are always capitalised when written. For example, Jane, Bangalore, Amazon
- Common Nouns: General names for people, places, things, or ideas. For example, woman, city, company
- Abstract Nouns: These are ideas or qualities that can be felt but not perceived by the five senses. For example, bravery, fear, happiness
- Concrete Nouns: These are objects that can be perceived by the senses. For example, chair, music
- Collective Nouns: These refer to a group of individuals or things. For example, a team of players, a flock of birds
- Countable or Uncountable Nouns: These refer to things or people that can or cannot be counted. Examples of countable nouns can be one book, two books, etc., whereas examples of uncountable nouns include water, advice, etc.
Pronouns – Substitutes for Nouns
Pronouns are words used in place of nouns to avoid repetition. They play a major role in simplifying the sentences and making them more understandable. They can be either a subject or an object in a sentence and perform as stand-ins for the nouns.
Types of Pronouns
There are seven major types of pronouns –
- Personal Pronouns: Refer to specific persons or things. For example, I, he, she, you, me, they
- Possessive Pronouns: These indicate ownership. For example, my, your, its, our, their, mine, yours
- Reflexive Pronouns: These are used to refer back to the subject of the sentence, indicating the subject reflecting on their action. For example, myself, himself, herself, itself
- Demonstrative Pronouns: These refer to specific people or things. For example, this, that, these, those
- Interrogative Pronouns: Used to ask questions. For example, who, what, whose, which
- Relative Pronouns: Used to connect a relative clause to a noun or pronoun. For example, who, whom, whose, which, that
- Indefinite Pronouns: Used to refer to non-specific persons or things. For example, all, any, some, everyone
What Is a Verb? – The Action Word
Verbs are used to express or describe an action. They indicate what the subject is doing or what state it is in. It is an essential part of speech in English, as no sentence can be complete without a verb.
Types of Verbs
Check out different types of verbs below –
- Action Verbs: They are used to describe a physical or mental action. There are two types of action verbs. The first type is a transitive verb that requires a direct object to complete its meaning. For example, the dog chased the cat. Here, to make sense of ‘chased’, we need the ‘cat.’
The other is an intransitive verb that does not require another object to complete its meaning. For example, the woman smiled.
- Linking Verbs: These are also known as state-of-being verbs and connect the subject to a noun, pronoun, or adjective that describes or identifies it. For example, to be, is, seems, become, etc.
- Auxiliary Verbs: Also known as helping verbs, they assist the main verb to express a mood or voice. For example, be, do, have, will, shall, may, can, must.
What Is an Adjective? – The Describing Word
Adjectives are words that modify or describe nouns or pronouns. They provide more information about their qualities, characteristics, or state. These are important parts of speech used to make descriptions more precise.
Types of Adjectives
- Descriptive Adjectives: Describe qualities. For example, beautiful, tall, intelligent
- Quantitative Adjectives: Indicate number or amount. For example, many, few, several
- Demonstrative Adjectives: Point out specific nouns. For example, this book, that car
- Possessive Adjectives: Indicates ownership. For example, my, your, his, her,
- Interrogative Adjectives: Used in questions to modify nouns. For example, which girl? What time?
- Articles: Used to specify whether a noun is general or specific. These include a, an, the
What Is an Adverb? – The Enhancer Word
Adverbs are used to modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They provide more meaning to the sentences and refine descriptions by adding the extent to which an action is performed..
Types of Adverbs
- Adverbs of Manner: How an action is done. For example, slowly, quickly, carefully
- Adverbs of Place: Where an action occurs. For example, here, there, everywhere, nearby
- Adverbs of Time: When an action occurs. For example, now, then, tomorrow, soon, later
- Adverbs of Frequency: How often an action occurs. For example, always, sometimes, never, often
- Adverbs of Degree: To what extent or intensity. For example, very, too, extremely, almost
What Is a Preposition? – The Relationship Word
Prepositions show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in the sentence. They often indicate location, direction, time, or manner.
Some common prepositions include – in, on, at, under, over, behind, with, for, from, to, about, during, through, across, beside, etc.
What Is a Conjunction? – The Joining Word
Conjunctions are words that join words, phrases, or clauses. They help in creating complex sentences and show logical relationships between different ideas.
Types of Conjunctions
Three types of conjunctions include –
- Coordinating Conjunctions: These connect words, phrases, or independent clauses of equal grammatical rank. These include – for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so.
- Subordinating Conjunctions: They connect a dependent clause to an independent clause. These include – because, since, although, while, when, if, unless, after, before
- Correlative Conjunctions: They work as a pair of conjunctions to connect sentences. Some examples include – either…or, neither…nor, both…and, not only…but also.
What Is an Interjection? – The Expressive Word
Interjections are words or short phrases that express strong emotion or surprise. They are used to make sentences more expressive. They are often followed by an exclamation mark and are independent of the rest of the sentence.
Some common interjections include – Oh!, Wow!, Ouch!, Hey!, Alas!, Hurray!, Oops!
Conclusion
How Do Parts of Speech Build Better Communication?
Parts of speech in English are the crucial building blocks for a strong grammatical foundation. In a world driven by communication, understanding what words play what role in a sentence enables one to communicate with confidence and precision.
Good IB schools in Bangalore, such as OWIS India, enable children to learn at their own pace and pay special attention to foundational concepts such as parts of speech to help them develop skills that will enable them to become smart, successful adults. So, get in touch with us today to understand how we can help your child’s development!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do IB schools in Bangalore teach grammar?
Through interactive activities, examples, and practical application.
When should children start learning parts of speech?
From primary school for stronger language foundations.
How can teachers make learning parts of speech fun?
By using storytelling, games, flashcards, and sentence-building activities.
How does learning parts of speech improve speaking skills?
It enables students to construct grammatically correct sentences and express ideas more clearly.
What is the difference between a verb and an adjective?
A verb describes an action or state, while an adjective describes a noun or pronoun.