Why Curriculums Matter
Curriculums can play a pivotal role in shaping a student’s future, both academically and professionally. They act as a guide, standardise learning objectives, ensure quality education, and provide flexibility for individualised learning. When choosing a school, understanding the school’s curriculum is the first step in the decision-making process.
Curriculums in Japan
For parents living in Japan, the education landscape offers diverse choices, including national and international schools, each with its unique benefits. National schools mainly follow Japan’s curriculum, immersing students in the local language, culture, and customs.
On the other hand, international schools provide students with a global perspective and proficiency in a second language. These schools are recognised for their accredited quality and their commitment to fostering both social and academic development. Therefore, choosing the right international school is an important decision for parents seeking a well-rounded educational experience.
Types of International School Curriculums

The landscape of international school curriculums is diverse and dynamic. When choosing the ‘right one,’ it’s essential to consider your child’s individual learning style, academic goals, and professional aspirations. However, it’s equally important to recognize that within each curriculum type, the rigour and focus of education can significantly vary depending on the specific school. In this comparative guide, we will delve into the various international school curriculums available in Japan, highlighting their distinct features. Some schools innovatively blend different educational philosophies and standards to create a unique learning environment.
International Baccalaureate (IB)
The International Baccalaureate (IB) program is a globally recognized educational curriculum. It offers students a comprehensive education, with a strong emphasis on the development of research, critical thinking, and communication skills.
The program is divided into four stages. The first stage is the Primary Years Programme (PYP), for ages 3 to 12. This stage is focused on establishing a foundation based on inquiry-based learning and personal development. It uses tailored learning methods, and provides a strong learning community, fostering curiosity and self-confidence in young children.
The second stage is the Middle Years Programme (MYP) for ages 11 to 16. It includes eight subject groups covering languages, humanities, sciences, maths, arts, physical education, and design. Students select one subject from each group, and through interactive learning and personal projects, students are able to make real-world connections.
At the age of 17, after completing the MYP, students can choose either:
・ The Diploma Program (DP) This prepares them for university studies, or:
・ The Career Program (CP). This focuses on a particular career path, by blending academic and practical skills
The International Baccalaureate program stands out as a worldwide renowned, adaptable educational curriculum. It empowers students to excel both academically and personally. This international school curriculum encourages students to become compassionate, impactful individuals.
Key Features
- Originating in Switzerland, the IB program curriculum is set and accredited by the International Baccalaureate Organization (IBO).
- The curriculum has been adopted worldwide, spanning over 168 countries. It is offered in three languages (English, Spanish, and French).
- There are more than 5,000 IB certified and accredited “IB world schools”. Students who relocate often can easily transfer credits and move between them.
- In addition to the foundational academic courses, it focuses on ensuring that students have communication, research and critical thinking skills.
- It also aims to develop personal and social skills that will allow students to adapt easily and quickly to changes in the world and effect change.
International Baccalaureate Diploma Program (IBDP)
Built from PYP and MYP, the IBDP is a specialised curriculum for students aged 16 to 19, equipping them with critical thinking, self-awareness, and research skills through practical core components like CAS, TOK, and EE.
- CAS (Creativity, Activity, Service): Requires students to engage in a variety of extracurricular and community service activities alongside academic coursework. CAS projects aim to challenge and transform students to develop skills like problem-solving, collaboration, and decision-making.
- Theory of Knowledge (TOK): Encourages students to reflect critically on the nature of knowledge and how we acquire it. Through discussions and assessments, they can summarise their learning, fostering self-awareness and critical thinking.
- EE (Extended Essay): Develops research and communication skills through in-depth, self-selected topics. The skills are beneficial for their future academic and professional endeavours.
The rigour of the IBDP is beneficial in helping students prepare for university, by developing discipline and time-management skills.
Key Features:
- The IDDP focuses on critical thinking, self-awareness, and research skills that can be applied to further studies and future careers.
- The DP diploma requires subject coursework, assessments, a 4,000-word essay, 150 hours of community service, and other mandatory classwork.
- The IDDP is recognized internationally by employers and is often used as a qualification for university admission.
- Students can choose between the DP, a general programme (or the CP which is more career-specific).
International Baccalaureate Diploma Program (IBDP) Bridging Program
The IB Bridging Programme is a short and intensive program designed to prepare students for transitioning into the International Baccalaureate (IB) Diploma Programme (DP).
As a bridge course, it helps students of all levels become familiar with the IB philosophy, teaching methods, and learning approaches. This thoroughly prepares them for the demands of the IB DP.
Key Features:
- The program is flexible and allows students to tailor their educational experience by choosing subject combinations that align with their capabilities and interests.
- The IB Bridging Programme has ongoing assessments throughout the year, so that evaluations of students progress is comprehensive and well-rounded.
- Students receive individual guidance and support through scheduled classes with subject teachers, covering content, skills, and concepts to help them understand and excel in DP courses.
- The program includes workshops that introduce students to essential IB DP core components, such as CAS, TOK, and EEs, preparing them for these integral aspects of the curriculum.
- Students also receive guidance in selecting courses and planning for their careers, ensuring a seamless transition to higher education and career pathways.
Montessori
The Montessori Curriculum is a child-centred, experiential approach for children of various ages, organised into multi-age classrooms, and emphasising individual needs and interests.
What makes it unique is its focus on concrete and experiential learning, with educational materials structured hierarchically and interrelated across different curriculum areas. It integrates subjects into five core areas: Practical Life, Sensorial, Mathematics, Language, and Culture.
In contrast to traditional schools, Montessori prioritises independence over memorization, and assesses through observations. Its benefits are increased self-confidence, critical thinking, customised education, inclusivity, and sensory and social development.
Key features:
- Freedom and Choice: Children choose their activities, fostering self-guided learning.
- Personalized Learning is tailored to each child’s development stage and needs.
- Experiential Learning that is hands-on, structured experiences that encourage exploration.
- Structured Materials that are organised hierarchically, promoting a structured foundation.
- Multi-Age Classes consist of mixed-age groups, encouraging peer learning and social development.
Cambridge Primary Programme (Cambridge PP)
Designed for children aged 5 to 11, the Cambridge Primary offers a well-rounded learning foundation, emphasising global topics and critical thinking.
In addition to core subjects like English, Mathematics, and Science, Cambridge Primary offers optional subjects, such as Music, Art and Design, Digital Literacy (IT), and Global Perspectives. This broad range of subjects enriches students’ learning experiences with diverse and transferable skills.
The Cambridge Primary Curriculum, from an early age, focuses on engaging and inspiring children, fostering creativity and innovation, while enhancing their independent thinking skills. This approach empowers students to develop a genuine passion for learning.
Key Features:
- Cambridge curriculum is used in over 160 countries worldwide, promoting a global community of learners and aligning with global perspectives.
- Cambridge Primary is flexible and can be integrated into various educational systems, including bilingual curriculums, while maintaining standardised academic aims and objectives.
- The curriculum is organised into six stages, each building on children’s knowledge from previous years.
- Cambridge Primary includes the unique subject of Global Perspectives, which fosters a global mindset and covers important international topics.
- Students go through assessments at each checkpoint to gauge their proficiency in core subjects, with an optional assessment available for Global Perspectives.
Cambridge Lower Secondary Programme (Cambridge CLSP)
The Cambridge CLSP is designed for learners aged 11 to 14 years old and acts as a bridge to help students transition from primary to secondary education.
The curriculum is diverse, with ten subjects, including core areas like English, mathematics, and science. This curriculum serves as a stepping stone, outlining the knowledge and skills students should acquire during the lower secondary phase. This effectively prepares them for the next stage, Upper Secondary, and A-levels through the Cambridge Advanced program.
Key Features:
- The Cambridge Lower Secondary curriculum is exceptionally flexible.
- It can be adapted and integrated into various educational programs, all while maintaining standardised global assessment objectives.
- The curriculum is closely aligned with the Cambridge Lower Secondary Progression Tests and Cambridge Lower Secondary Checkpoint, ensuring that learners are evaluated based on the content covered in the classroom.
Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (IGCSE) curriculum
Cambridge IGCSE is a globally recognised educational program designed for students aged 14 to 16. It provides a high-quality international qualification with a wide range of subject choices. It also thoroughly prepares students for their future studies, after the age of 16.
It is renowned for its comprehensive curriculum and international recognition, aligning with the standards of the GCSE qualification in England. It caters to a diverse range of abilities, including students whose first language is not English.
With over 70 subjects, including 30 languages, and flexibility in subject combinations, it offers students a wide array of choices to tailor their education to their interests and future goals.
Cambridge IGCSE is recognised for prioritising learner-centred and inquiry-based learning, fostering creative thinking and problem-solving skills, making it effective in preparing students for the next stage in their education.
Key Features:
- Wide Subject Choice: Over 70 subjects, including language options.
- Develops critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Adaptable: Offers both Core and Extended curriculum to suit different abilities.
- Accepted by universities and employers worldwide.
- Holistic Approach: Promotes all-around development through various activities and projects.
The American Common Core
The American curriculum is a well-structured and widely recognized educational framework, primarily designed to prepare students for success in college and the workplace.
The curriculum is divided into three levels: Elementary School, Middle School, and High School. Each level is designed to progressively challenge students and develop their skills and knowledge in a wide range of subjects like English, maths, science, social studies and physical education.
The curriculum focuses on independent learning and encourages students to take ownership of their education through projects, collaboration, and research. Students are usually supported by having access to high-quality technology, libraries, research facilities and other resources.
The American curriculum is recognised for providing a diverse range of academic subjects and co-curricular activities in sports and the performing arts. Students are also encouraged to develop interests and skills beyond academics, by participating in extracurricular activities and community service. This further advances the holistic, well-rounded education students can receive.
It is an attractive option for many parents seeking a high-quality education for their children, whether they are in the United States or at international schools abroad.
Key Features:
- Focus on independent thinking and individualised learning.
- Global Recognition of American high school diplomas.
- Flexible curriculum tailored to individual needs.
- Focus on critical thinking, creativity, and social skills.
- Comprehensive Subject Offering: The American curriculum offers a diverse range of subjects, including core subjects and electives. This allows students to explore their personal interests and individual talents.
The Indian Curriculum (CBSE)
The Indian curriculum, under the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) refers to the curriculum used by schools in India.
It consists of core and elective subjects, practical knowledge, and co-curricular activities aimed to provide students with a wide range of skills including critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration.
The Indian curriculum is divided into three levels:
- Primary (ages 6 to 12), students study subjects such as mathematics, science, social studies, and languages.
- Secondary (ages 13 to 15), students study more advanced subjects like physics, chemistry, biology, history and geography
- Higher secondary (ages 17 and 18). Students have the option to choose elective subjects based on their interests and career goals
The Indian curriculum is known for its emphasis on academic excellence, preparing students for success in higher education and the workplace. In addition to establishing a solid academic groundwork, it also cultivates their skills as innovative, critical thinkers, enabling them to confront challenges in the global landscape.
- Holistic Approach: It offers a well-rounded education, covering various subjects and co-curricular activities.
- Continuous Evaluation: It emphasises year-round assessment rather than relying solely on year-end exams.
- Life Skills: It integrates critical life skills development, such as problem-solving and communication.
- Flexibility: Students have subject choices at the senior secondary level to align with their interests and career goals.
- Technology Integration: CBSE promotes the use of technology in teaching and learning for a modern and engaging education.
British National Curriculum
The British National Curriculum, (the National Curriculum of England), is a standardised program used by primary and secondary schools in England. It consists of a structured and standard set of subjects, with a strong emphasis on building foundational skills in reading, writing and arithmetic.
It is known for its academic rigour, and developing skills that students can build on and use to succeed in further education and employment. Each subject has detailed guidelines on the learning objectives of each subject at each key stage, however schools have flexibility in teaching methods. The British National Curriculum is structured into various key stages (with four Key stages that cater to students aged 5 to 16 ) based on age groups and educational levels.
- The Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS) is for children aged 3 to 5, in nursery schools and focuses on developing key skills, personal, social, and emotional development.
- Key Stage 1 (KS1): Ages 5 to 7 and Years 1 and 2 in primary school. It teaches subjects like English, mathematics, science, art, design and technology, geography, history, and physical education (PE).
- Key Stage 2 (KS2): Ages of 7 and 11, and Years 3 to 6 in primary school. Building on the foundation of KS1, it introduces more advanced topics in various subjects.
- Key Stage 3 (KS3): Ages 11 to 14 and is taught in secondary schools. The curriculum is broad and balanced. It includes core subjects like English, mathematics, and science, as well as other subjects like geography, history, modern foreign languages, and art.
- Key Stage 4 (KS4): Ages 14 to 16 and is usually the last stage of mandatory education. Students take the General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) examinations, in various subjects.
The curriculum provides students with a well-rounded education, building skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication that can be used throughout their lives. Students can also develop an understanding of diverse cultures and perspectives as well as address modern issues like climate change and digital literacy.
Key Features:
- The British National Curriculum is recognised in over 160 countries by more than 30,000 schools.
- The curriculum is student-centred and focuses on literacy, critical thinking, problem-solving, and independent learning, preparing students for further education and employment.
- The four key stages are: EYFS, KS1, KS2, and KS3.
- Courses are taught through a combination of lectures, group discussions, practical activities, and individual study.
- In the early stages, there are no formal tests. Standardised tests and exams are introduced later on. Lastly, students can earn qualifications like the GCSE and A-level
Comparing and Choosing a Curriculum
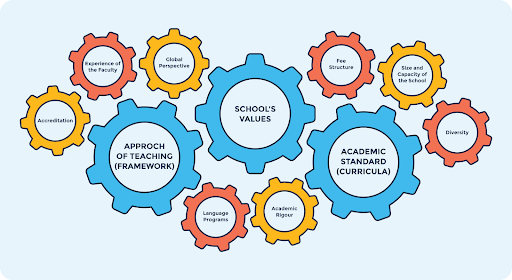
When comparing various international school curriculums, it’s crucial to discern both the distinct characteristics and commonalities they share. The International Baccalaureate (IB) and the Cambridge curricula both underscore the importance of critical thinking and a global perspective, with the IB providing a more structured educational framework.
On the other hand, the American Common Core is known for its flexibility and emphasis on independent learning. The Montessori method is renowned for its experiential and individualised learning approach. The Indian Curriculum(CBSE) focuses on continuous assessment and life skills development. The British National Curriculum is globally recognized for its comprehensive and balanced educational approach.
Despite these differences, a common thread among these curricula is their commitment to holistic development, equipping students with the necessary skills to navigate future challenges. When choosing a school, there are various factors to think about. These critical considerations may include
the school’s underlying philosophy, the qualifications and experience of the faculty, the fee structure, the size and capacity of the school, the availability and diversity of language programs, and the school’s commitment to fostering a global outlook. Understanding these aspects will guide parents and students in making an informed decision that aligns with their educational priorities, financial considerations, and personal aspirations
Importance of a Multicultural and Global Perspective

In today’s globalised world, international school curriculums are pivotal in shaping broad-minded citizens. Many of the International school curriculums mentioned expose students to diverse cultures, global perspectives and second languages.
Students not only have a wide world view through the curriculum but also through interactions with classmates and teachers. A global perspective equips students to adapt in our interconnected world to drive positive change. This is increasingly important and can lead to a brighter future for everyone.
Holistic Education Approach in International Curriculums
International school curriculums also go beyond teaching foundational subjects, but also provide a well-rounded education for students that goes beyond traditional academics. Students can develop skills like critical thinking, problem-solving, and awareness of global dynamics. The curriculums also nurture personal and social skills, promote adaptability, and instil values like caring, open-mindedness, and responsible behaviour as essential traits for global citizens.
Conclusion
In conclusion, international school curriculums play an important role in providing students with a well-rounded education and preparing them to become active and informed global citizens. These curriculums not only cover the core academic subjects but also emphasise vital transferable skills. They are organised into various educational stages, employ diverse teaching methods, and use alternative assessment approaches.
International school curriculums are often recognized globally, making them suitable for foreign nationals and internationally-minded students. These curriculums aim to develop international exposure, language proficiency, and skills to address global challenges, as well as promoting inclusivity, cultural understanding, and essential transferable skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, research, and collaboration.